Creating your first JavaFX chart app, part 3
This third tutorial details charts events and interactions.
This tutorial will help you understand:
- What are the different chart events
- How-to listen to events
- How-to push events
What do you need?
- 15 minutes
- A working JavaFX environment (see part 1)
- Intellij Community or Ultimate (tested with IntelliJ 2020.3.*)
The chart events
There are 4 chart events you can bind on, here is a cheat sheet presenting all of them:
Highlight event
- This event is a Data Event, it takes and returns
DOMAINobjects - This event is enabled by default, disable it with
config.events.highlightMode - Listen:
chart.onHighlight(listener: (event: HighlightEvent<DOMAIN>) -> Unit) - Push:
chart.highlight(domains: Collection<DOMAIN>)orchart.highlight(data: Collection<Datum<DOMAIN>>)
Select event
- This event is a Data Event, it takes and returns
DOMAINobjects - This event is disabled by default, disable it with
config.events.selectionMode - Listen:
chart.onSelect(listener: (event: SelectEvent<DOMAIN>) -> Unit) - Push:
chart.select(domains: Collection<DOMAIN>)orchart.select(data: Collection<Datum<DOMAIN>>)
Zoom event
- This event is a View Event, it applies transformation to the current charting zone
- This event is disabled by default, disable it with
config.events.zoomMode - Listen:
chart.onZoom(listener: (event: ZoomEvent) -> Unit) - Push:
chart.zoom(zoomOriginX, zoomOriginY, zoomFactorX, zoomFactorY)
Pan event (scroll event)
- This event is a View Event, it applies transformation to the current charting zone
- This event is disabled by default, disable it with
config.events.panMode - Listen:
chart.onPan(listener: (event: PanEvent) -> Unit) - Push:
chart.pan(panX: Percent, panY: Percent)
Chart events types
As their name implies, data events take and return "data".
You can trigger an on-screen selection by calling chart.select() with a list of DOMAIN objects.
Similarly, when a user selects stuff on screen, you can retrieve the list of underlying domain objects by listening to the SelectEvent.
View events are related to the "view" of your chart, the main drawing zone, here, in blue.
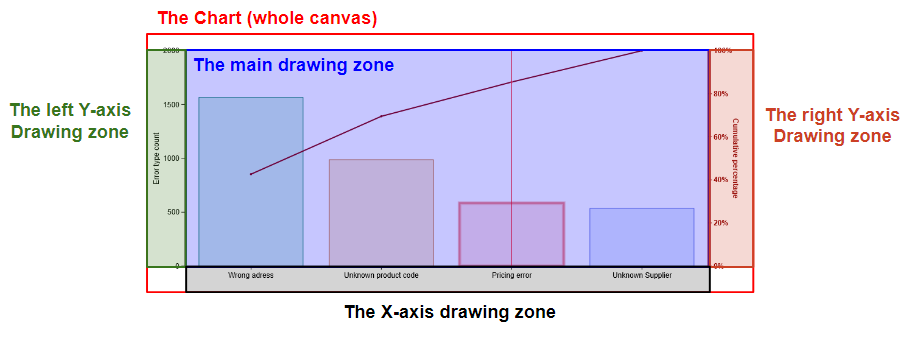
View events do not return data but rather indicate how much the view has changed from its initial position.
Receiving and pushing chart events
Listening to events
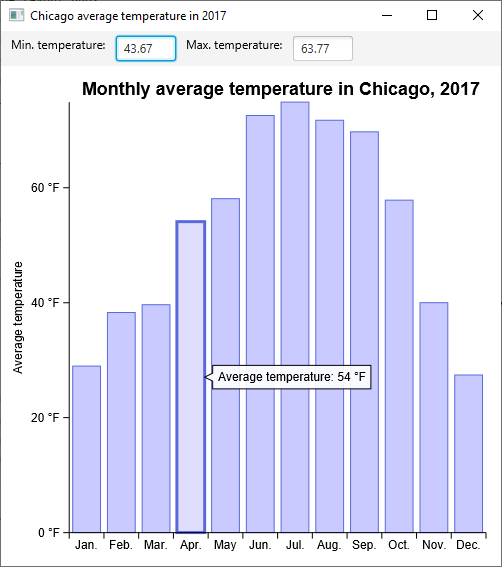
From the previous "weather app" (see part 2) we want to add 2 input fields inputMin and inputMax to display the min and max temperature of a highlighted item.
Create these fields, then create a function that takes 2 Double and displays their values in the corresponding fields, let's call this function updateFields:
import com.sun.javafx.scene.control.DoubleField
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.Chart
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.chart
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.discrete
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.mark.bar
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.quantitative
import io.data2viz.charts.core.formatToInteger
import io.data2viz.charts.event.HighlightEvent
import io.data2viz.charts.viz.VizContainer
import io.data2viz.charts.viz.newVizContainer
import io.data2viz.format.Locales
import io.data2viz.geom.Size
import javafx.application.Application
import javafx.geometry.Insets
import javafx.scene.Scene
import javafx.scene.layout.HBox
import javafx.scene.layout.Pane
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox
import javafx.scene.text.Text
import javafx.stage.Stage
import java.io.File
fun main() {
Application.launch(EventsChart::class.java)
}
private val width = 500.0
private val height = 700.0
private val months =
listOf("Jan.", "Feb.", "Mar.", "Apr.", "May", "Jun.", "Jul.", "Aug.", "Sep.", "Oct.", "Nov.", "Dec.")
private val city = "Chicago"
private val year = 2017
private fun loadData(): List<Weather> {
val csvContent = File("./src/main/resources/Weather - Stats.csv").readText()
val weatherData = parseWeatherCSV(csvContent)
val filteredData = weatherData.filter { weather: Weather ->
weather.city == city && weather.year == year
}
return filteredData
}
class EventsChart : Application() {
override fun start(stage: Stage) {
val chicago2017 = loadData()
val root = VBox()
val dataBox = HBox().apply {
padding = Insets(5.0, 10.0, 5.0, 10.0)
spacing = 10.0
}
val inputMin = DoubleField().apply {
isEditable = false
maxWidth = 60.0
}
val inputMax = DoubleField().apply {
isEditable = false
maxWidth = 60.0
}
dataBox.children.addAll(
Text("Min. temperature:"),
inputMin,
Text("Max. temperature:"),
inputMax
)
root.children.add(dataBox)
val chartPane = Pane()
root.children.add(chartPane)
val updateFields = { min: Double, max: Double ->
inputMin.value = min
inputMax.value = max
}
chartPane.newVizContainer().run {
size = Size(width, height)
createChart(chicago2017, updateFields)
}
// Launch our Scene
stage.apply {
title = "Chicago average temperature in 2017"
scene = (Scene(root, width, height))
show()
}
}
private fun VizContainer.createChart(chicago2017: List<Weather>, callback: (Double, Double) -> Unit): Chart<Weather> =
chart(chicago2017) {
title = "Monthly average temperature in $city, $year"
val monthDimension = discrete({ domain.month }) {
formatter = { months[this - 1] }
}
val temperatureDimension = quantitative({ domain.avgTemp }) {
name = "Average temperature"
formatter = { "${this.formatToInteger(Locales.en_US)} °F" }
}
bar(monthDimension, temperatureDimension) {
onHighlight { event: HighlightEvent<Weather> ->
val domain = event.data.firstOrNull()?.domain
callback(domain?.lowTemp ?: .0, domain?.highTemp ?: .0)
}
}
}
}
Now pass this function to your chart and plug-it on an onHighlight listener.
The HighlightEvent contains a data property, which is here a Collection<Datum<Weather>>.
On a bar chart your visuals don't overlap, meaning you can't highlight 2 different items, so this collection is whether empty or contains a single element.
Just take this element and pass the min and max temperature to the callback function.
import com.sun.javafx.scene.control.DoubleField
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.Chart
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.chart
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.discrete
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.mark.bar
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.quantitative
import io.data2viz.charts.core.formatToInteger
import io.data2viz.charts.event.HighlightEvent
import io.data2viz.charts.viz.VizContainer
import io.data2viz.charts.viz.newVizContainer
import io.data2viz.format.Locales
import io.data2viz.geom.Size
import javafx.application.Application
import javafx.geometry.Insets
import javafx.scene.Scene
import javafx.scene.layout.HBox
import javafx.scene.layout.Pane
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox
import javafx.scene.text.Text
import javafx.stage.Stage
import java.io.File
fun main() {
Application.launch(EventsChart::class.java)
}
private val width = 500.0
private val height = 700.0
private val months =
listOf("Jan.", "Feb.", "Mar.", "Apr.", "May", "Jun.", "Jul.", "Aug.", "Sep.", "Oct.", "Nov.", "Dec.")
private val city = "Chicago"
private val year = 2017
private fun loadData(): List<Weather> {
val csvContent = File("./src/main/resources/Weather - Stats.csv").readText()
val weatherData = parseWeatherCSV(csvContent)
val filteredData = weatherData.filter { weather: Weather ->
weather.city == city && weather.year == year
}
return filteredData
}
class EventsChart: Application() {
override fun start(stage: Stage) {
val chicago2017 = loadData()
val root = VBox()
val dataBox = HBox().apply {
padding = Insets(5.0, 10.0, 5.0, 10.0)
spacing = 10.0
}
val inputMin = DoubleField().apply {
isEditable = false
maxWidth = 60.0
}
val inputMax = DoubleField().apply {
isEditable = false
maxWidth = 60.0
}
dataBox.children.addAll(
Text("Min. temperature:"),
inputMin,
Text("Max. temperature:"),
inputMax
)
root.children.add(dataBox)
val chartPane = Pane()
root.children.add(chartPane)
val updateFields = { min: Double, max: Double ->
inputMin.value = min
inputMax.value = max
}
chartPane.newVizContainer().run {
size = Size(width, height)
createChart(chicago2017, updateFields)
}
// Launch our Scene
stage.apply {
title = "Chicago average temperature in 2017"
scene = (Scene(root, width, height))
show()
}
}
private fun VizContainer.createChart(chicago2017: List<Weather>, callback: (Double, Double) -> Unit): Chart<Weather> =
chart(chicago2017) {
title = "Monthly average temperature in $city, $year"
val monthDimension = discrete({ domain.month }) {
formatter = { months[this - 1] }
}
val temperatureDimension = quantitative({ domain.avgTemp }) {
name = "Average temperature"
formatter = { "${this.formatToInteger(Locales.en_US)} °F" }
}
bar(monthDimension, temperatureDimension) {
onHighlight { event: HighlightEvent<Weather> ->
val domain = event.data.firstOrNull()?.domain
callback(domain?.lowTemp ?: .0, domain?.highTemp ?: .0)
}
}
}
}
Create a new EventsChart.kt file and paste this code (click on the "+" icon to see the full code), then run your application, you should see the result:
Pushing events
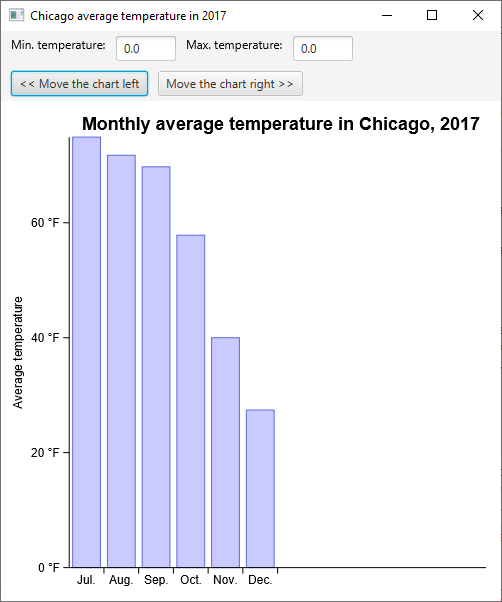
Let's say that your application handles scrolling so you want to disable pan in your chart, and control it from your app.
Add a second HBox to your app with 2 buttons: moveLeft and moveRight.
Each of these buttons will "pan" the chart's view by 1/12 (8.33%):
import com.sun.javafx.scene.control.DoubleField
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.Chart
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.chart
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.discrete
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.mark.bar
import io.data2viz.charts.chart.quantitative
import io.data2viz.charts.core.formatToInteger
import io.data2viz.charts.event.HighlightEvent
import io.data2viz.charts.viz.VizContainer
import io.data2viz.charts.viz.newVizContainer
import io.data2viz.format.Locales
import io.data2viz.geom.Size
import io.data2viz.math.pct
import javafx.application.Application
import javafx.event.ActionEvent
import javafx.event.EventHandler
import javafx.geometry.Insets
import javafx.scene.Scene
import javafx.scene.control.Button
import javafx.scene.layout.HBox
import javafx.scene.layout.Pane
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox
import javafx.scene.text.Text
import javafx.stage.Stage
import java.io.File
fun main() {
Application.launch(EventsChart::class.java)
}
private val width = 500.0
private val height = 500.0
private val months =
listOf("Jan.", "Feb.", "Mar.", "Apr.", "May", "Jun.", "Jul.", "Aug.", "Sep.", "Oct.", "Nov.", "Dec.")
private val city = "Chicago"
private val year = 2017
private fun loadData(): List<Weather> {
val csvContent = File("./src/main/resources/Weather - Stats.csv").readText()
val weatherData = parseWeatherCSV(csvContent)
val filteredData = weatherData.filter { weather: Weather ->
weather.city == city && weather.year == year
}
return filteredData
}
class EventsChart : Application() {
override fun start(stage: Stage) {
val chicago2017 = loadData()
val root = VBox()
val dataBox = HBox().apply {
padding = Insets(5.0, 10.0, 5.0, 10.0)
spacing = 10.0
}
val inputMin = DoubleField().apply {
isEditable = false
maxWidth = 60.0
}
val inputMax = DoubleField().apply {
isEditable = false
maxWidth = 60.0
}
dataBox.children.addAll(
Text("Min. temperature:"),
inputMin,
Text("Max. temperature:"),
inputMax
)
root.children.add(dataBox)
val panBox = HBox().apply {
padding = Insets(5.0, 10.0, 5.0, 10.0)
spacing = 10.0
}
val moveLeft = Button("<< Move the chart left")
val moveRight = Button("Move the chart right >>")
panBox.children.addAll(moveLeft, moveRight)
root.children.add(panBox)
val chartPane = Pane()
root.children.add(chartPane)
val updateFields = { min: Double, max: Double ->
inputMin.value = min
inputMax.value = max
}
val weatherChart = chartPane.newVizContainer().run {
size = Size(width, height)
createChart(chicago2017, updateFields)
}
moveLeft.onMouseClicked = EventHandler {
weatherChart.pan((-8.333).pct, 0.pct)
}
moveRight.onMouseClicked = EventHandler {
weatherChart.pan(8.3333.pct, 0.pct)
}
// Launch our Scene
stage.apply {
title = "Chicago average temperature in 2017"
scene = (Scene(root, width, height))
show()
}
}
private fun VizContainer.createChart(chicago2017: List<Weather>, callback: (Double, Double) -> Unit): Chart<Weather> =
chart(chicago2017) {
title = "Monthly average temperature in $city, $year"
val monthDimension = discrete({ domain.month }) {
formatter = { months[this - 1] }
}
val temperatureDimension = quantitative({ domain.avgTemp }) {
name = "Average temperature"
formatter = { "${this.formatToInteger(Locales.en_US)} °F" }
}
bar(monthDimension, temperatureDimension) {
onHighlight { event: HighlightEvent<Weather> ->
val domain = event.data.firstOrNull()?.domain
callback(domain?.lowTemp ?: .0, domain?.highTemp ?: .0)
}
}
}
}
By default, panning is disabled in your chart: this concerns the user interactions. Your users cannot scroll in the chart, still, you can always call
chart.pan()and control the scroll from your application.
Replace your code with the code above and run the application, you now should be able to move your chart right and left by clicking on the buttons: